本章通过链表实现栈这一数据结构
- 链表
链表之前也写了很多文章介绍了,这里基本信息略过,感兴趣的可以去之前的文章了解一下,我这里就假设你们已经对链表和栈很熟悉了。
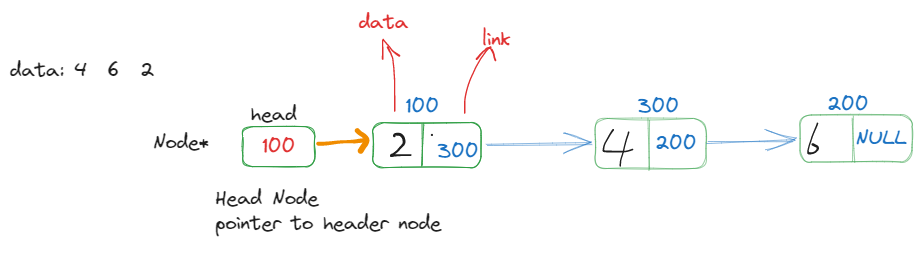
push在数组中只有一种情况,因为数组是连续的内存空间1,而链表则是根据不同地址的节点链接在一起的,所以这时候我们就要考虑两种情况了。头部插入或者是尾部插入,尾部插入需要遍历链表所以他的复杂度是O(n),如果是从头部插入的话复杂度假设O(1),所以我们选择从头部插入。链表的插入我们已经很清楚了,这里就直接看代码如何实现栈。

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* link;
};
Node* top = NULL;
void push(int x);
void pop();
int Top();
void Isempty();
int main()
{
push(2);
push(5);
}
void push(int x)
{
Node*temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = x;
temp->link = top;
top = temp;
}
void pop()
{
Node* temp = top;
if (top==NULL)
{
return;
}
top = temp->link;
free(temp);
}
int Top()
{
Node* temp = top;
return temp->data;
}
void Isempty()
{
if (top == NULL)
{
printf("yes");
}
else
{
printf("no");
}
}