运算符重载是一种形式的c++多态,上一张笔记的函数重载也可以叫做函数多态,运算符重载将重载的概念扩展到运算符上,允许C++运算符有多种含义。很多C++运算符已经被重载,例如 将解引用符号*,但他用于数值之间就是乘积,C++根据操作数的数目和类型来决定采用哪种操作。
C++允许将运算符重载扩展到我们自己定义的类型,例如可以让两个对象相加,编译器根据操作数的数目和类型决定使用哪种加法定义。
例:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
int a[10];
int b[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int c[10] = { 11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 };
for (size_t i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
a[i] = b[i] + c[i];
}
}也可以重载加法运算符,并用表示数组的类相加,
如 c = a + b
要重载运算符,需使用被称为运算符函数的特殊函数形式,operatorop(argument-list)
例如 operator+()表示重载+运算符, operator*()表示重载*运算符,op必须是有效的C++运算符,斌是虚构的符号 如@等。
operator[]()重载[]运算符,因为[]是数组索引运算符
如果有一个类,重载了+运算符,使得数据求和可以通过对象直接相加 比如
#include<iostream>
class Salesperson
{
public:
Salesperson(int n = 5);
Salesperson()
{
sale = 0;
}
int operator +(const Salesperson&t);
private:
int sale;
};
Salesperson::Salesperson(int n)
{
sale = n;
}
int Salesperson::operator+(const Salesperson& t)
{
int sale = this->sale + t.sale;
return sale;
}
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Salesperson s1(10);
Salesperson s2(20);
int ret = s1 + s2;
cout << ret << endl;
}结果是30 因为编译器发现是类对象,符合我们重载函数的特征标,因此重载运算符函数就变成了 sale = s1.operator+(s2) 显式地调用s2对象,可以简单地使用运算符表示。
然后我们会再通过一些例子深入了解运算符重载以及一些限制
计算时间(运算重载示例)
例子来源C++ Primer Plus(第6版)可以到我的资源站下载哦!
书上的翻译太拗口了,我直接改编一下,我早上花了2个小时40分钟用来健身,下午花费了2小时35分健身,猛男嘛!理解一下。如果我们想知道花了多少时间,加法是最合适的,但问题是他们的类型也不同,我们将使用Time类进行计算。
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
class Time
{
public:
Time();
~Time();
Time(int h, int m = 0);
void AddMin(int m);
void Addhour(int h);
void reset(int h = 0, int m = 0);
Time Sum(const Time& T)const;
void show()const;
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
};#include "Time.h"
Time::Time()
{
hours = minutes = 0;
}
Time::~Time()
{
}
Time::Time(int h, int m)
{
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
void Time::AddMin(int m)
{
minutes += m;
hours += minutes / 60;
minutes %= 60;
}
void Time::Addhour(int h)
{
hours += h;
}
void Time::reset(int h, int m)
{
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
Time Time::Sum(const Time& T) const
{
Time sum;
sum.minutes = minutes + T.minutes;
sum.hours = hours + T.hours + sum.minutes / 60;
sum.minutes %= 60;
return sum;
}
void Time::show() const
{
std::cout << hours << " hours," << minutes << " minutes";
}#include"Time.h"
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Time planning;
Time p1(2, 40);
Time p2(5, 55);
Time total;
cout << "planning time = ";
planning.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "p1 time = ";
p1.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "p2 time = ";
p2.show();
cout << endl;
total = p1.Sum(p2);
cout << "p1.sum(p2) = ";
total.show();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}首先看一下算法,满60分钟是一小时 所以minutes/60就是分钟的小时 而minutes%=60 是模运算,为了计算分钟数
注意函数返回值不可以是引用,因为引用就是sunm,sum在函数执行完成之后就被销毁了,而如果返回Time,则回调用默认构造函数 调用函数将得到它的拷贝( 当用一个对象去初始化同类的另一个对象时,会引发复制构造函数被调用。例如,下面的两条语句都会引发复制构造函数的调用,用以初始化 total)
添加加法运算符
修改我们之前写的成员函数sum改为重载加法运算符
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
class Time
{
public:
Time();
Time(int h, int m = 0);
void AddMin(int m);
void Addhour(int h);
void reset(int h = 0, int m = 0);
Time operator+(const Time& T)const;
void show()const;
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
};此时operator+()也是由Time对象调用的,因此可以
total = p1.operator+(p2);
也可以用
total = p1+p2;然后我们修改main.cpp文件然后调用它
#include"Time.h"
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Time planning;
Time p1(2, 40);
Time p2(5, 55);
Time total;
cout << "planning time = ";
planning.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "p1 time = ";
p1.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "p2 time = ";
p2.show();
cout << endl;
total = p1 + p2;
cout << "p1.sum(p2) = ";
total.show();
cout << endl;
Time moren(3,28);
cout << "moren time = ";
moren.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "total.operator+(morn) = ";
total = total.operator+(moren);
total.show();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}Time A,B,C
A+B+C这样做合法吗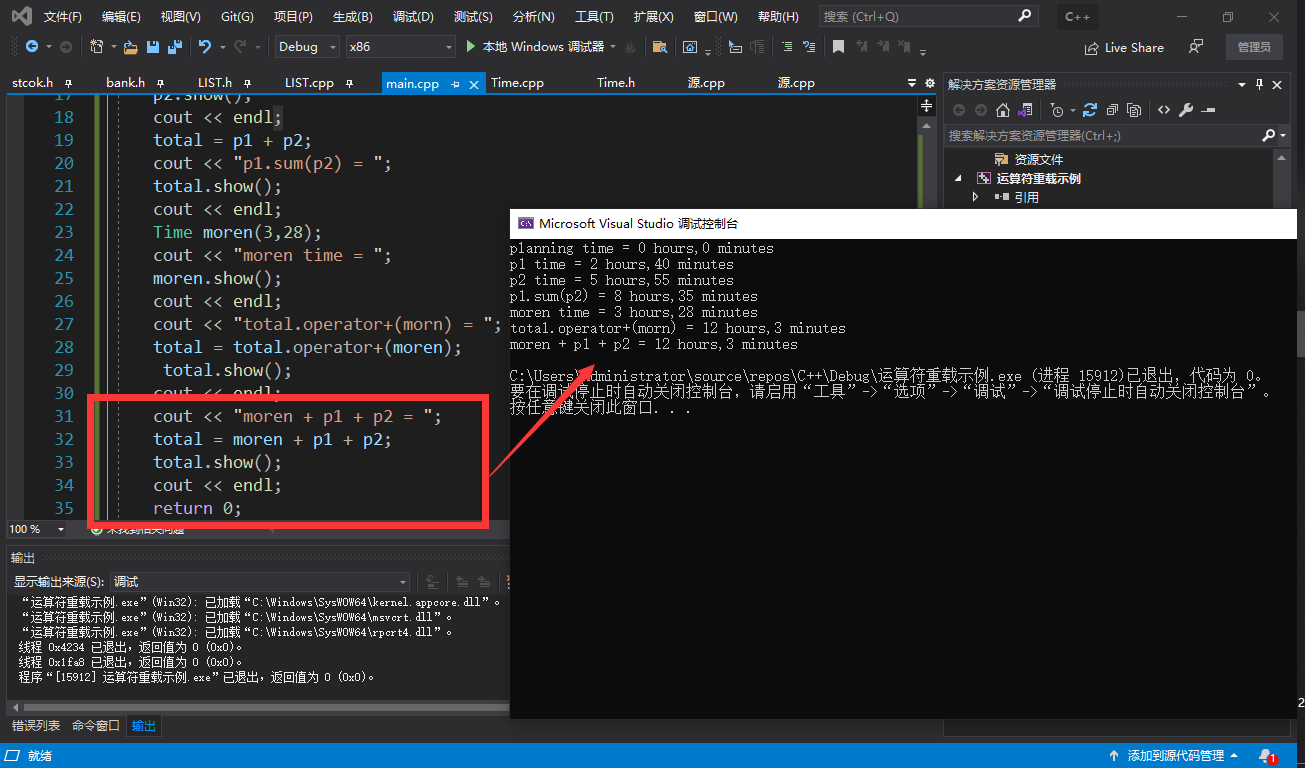
转换一下函数表示法:A.operator+(B.operator+(C));
重载限制
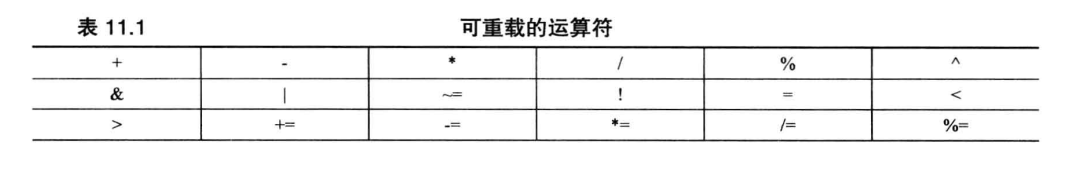
多数C++运算符都可以用这样的方式重载,重载运算符不必是成员函数,但必须至少有一个是用户定义的类型。
- 至少有一个操作数是用户自定义类型,防止重载标准类型的运算符
- 使用运算符不能违反运算符原来的句法规则。例如,不能将2求模运算符重载为使用一个操作数 ,同样也不能修改运算符的优先级,比如重载加号 重载后优先级和加号优先级一样
- 不能创建新运算符
- 不能重载以下列举的运算符
sizeof . .* :: ? typeid const_cast dynamic_cast reinterpret_cast static_cast
5.下面将列举的是只能通过成员函数重载的运算符
= () [] ->
下表是既可以通过成员函数也可以通过非成员函数重载的运算符
重载其他运算符
- 两个时间可能相减
- 时间乘以一个因子
修改后的Time.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
class Time
{
public:
Time();
Time(int h, int m = 0);
void AddMin(int m);
void Addhour(int h);
void reset(int h = 0, int m = 0);
Time operator+(const Time& T)const;
Time operator-(const Time & T)const;
Time operator*(double n)const;
void show()const;
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
};这里仅就新重载的两条代码进行代码定义
Time Time::operator*(double n) const
{
Time res;
long totalminutes = hours * n * 60 + minutes * n;
res.hours = totalminutes / 60;
res.minutes = totalminutes % 60;
return res;
}
Time Time::operator-(const Time& T) const
{
Time sum;
int t1, t2;
t1 = minutes + 60 * hours;
t2 = T.minutes + 60 * T.hours;
sum.hours = (t1 - t2) / 60;
sum.minutes = (t1 - t2) % 60;
return sum;
}然后就可以修改main.cpp
#include"Time.h"
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Time planning;
Time p1(4, 35);
Time p2(2, 47);
Time total;
cout << "planning time = ";
planning.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "p1 time = ";
p1.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "p2 time = ";
p2.show();
cout << endl;
total = p1 + p2;
cout << "p1.sum(p2) = ";
total.show();
cout << endl;
Time moren(3,28);
cout << "moren time = ";
moren.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "total.operator+(morn) = ";
total = total.operator+(moren);
total.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "moren + p1 + p2 = ";
total = moren + p1 + p2;
total.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "p1-p2 = ";
total = p1 - p2;
total.show();
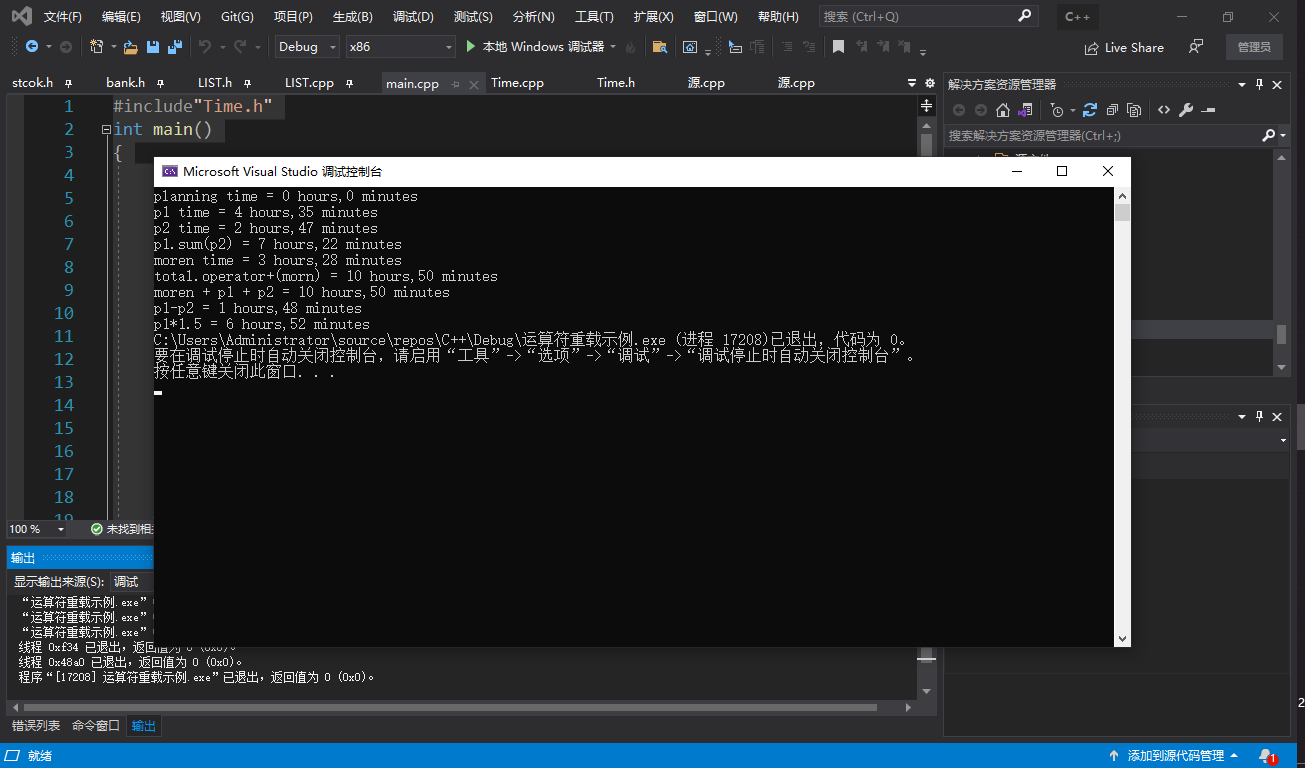
cout << endl;
cout << "p1*1.5 = ";
total = p1 * 1.5;
total.show();
return 0;
}运行截图